Recent Aspects of Pulmonary Drug Delivery System - An Overview
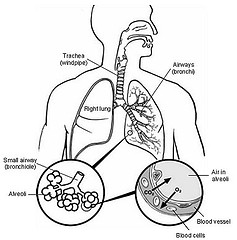
Pulmonary delivery of drugs has become an attractive target in the health care industry as the lung is capable of absorbing pharmaceuticals either for local deposition or for systemic delivery. Half of all pharmaceuticals are not soluble in water, but are soluble in lipid. As the lung is able to absorb both water and oil into the tissue, this is not a limitation of pulmonary delivery. However, existing jet nebulizers cannot aerosolize viscous liquids and ultrasound nebulizers destroy drug emulsions, thereby greatly limiting the potential use of pulmonary drug delivery.
The whole 17 pages article is available for download here.